Devotional Bharat
Anatomically modern humans are thought to have arrived in South Asia 73–55,000 years back,[20] though the earliest authenticated human remains date to only about 30,000 years ago.[21] Nearly contemporaneous Mesolithic rock art sites have been found in many parts of the Indian subcontinent, including at the Bhimbetka rock shelters in Madhya Pradesh.[22] Around 7000 BCE, the first knownNeolithic settlements appeared on the subcontinent in Mehrgarh and other sites in western Pakistan.[23] These gradually developed into the Indus Valley Civilisation,[24] the first urban culture in South Asia;[25] It flourished during 2500–1900 BCE in Pakistan and western India.[26] Centred around cities such as Mohenjo-daro, Harappa, Dholavira, and Kalibangan, and relying on varied forms of subsistence, the civilisation engaged robustly in crafts production and wide-ranging trade.[25]
During the period 2000–500 BCE, in terms of culture, many regions of the subcontinent transitioned from the Chalcolithic to the Iron Age.[27] The Vedas, the oldest scriptures of Hinduism,[28] were composed during this period,[29] and historians have analysed these to posit a Vedic culture in the Punjab region and the upper Gangetic Plain.[27] Most historians also consider this period to have encompassed several waves of Indo-Aryan migration into the subcontinent from the north-west.[30][28][31] The caste system, which created a hierarchy of priests, warriors, and free peasants, but which excluded indigenous peoples by labelling their occupations impure, arose during this period,[32] and small tribal units gradually coalesced into monarchical, state-level polities.[33] On the Deccan Plateau, archaeological evidence from this period suggests the existence of a chiefdom stage of political organisation.[27] In southern India, a progression to sedentary life is indicated by the large number of megalithic monuments dating from this period,[34] as well as by nearby traces of agriculture, irrigation tanks, and craft traditions.[34]
In the late Vedic period, around the 5th century BCE, the small states and chiefdoms of the Ganges Plain and the north-western regions had consolidated into 16 major oligarchies and monarchies that were known as the mahajanapadas.[35][36] The emerging urbanisation and the orthodoxies of this age also created heterodox religious movements, two of which became independent religions. Buddhism, based on the teachings of Gautama Buddha attracted followers from all social classes excepting the middle class; chronicling the life of the Buddha was central to the beginnings of recorded history in India.[37][38][39] Jainism came into prominence during the life of its exemplar, Mahavira.[40] In an age of increasing urban wealth, both religions held up renunciation as an ideal,[41] and both established long-lasting monastic traditions. Politically, by the 3rd century BCE, the kingdom of Magadha had annexed or reduced other states to emerge as the Mauryan Empire.[35] The empire was once thought to have controlled most of the subcontinent excepting the far south, but its core regions are now thought to have been separated by large autonomous areas.[42][43] The Mauryan kings are known as much for their empire-building and determined management of public life as for Ashoka's renunciation of militarism and far-flung advocacy of the Buddhist dhamma.[44][45]
The Sangam literature of the Tamil language reveals that, between 200 BCE and 200 CE, the southern peninsula was being ruled by the Cheras, theCholas, and the Pandyas, dynasties that traded extensively with the Roman Empire and with West and South-East Asia.[46][47] In North India, Hinduism asserted patriarchal control within the family, leading to increased subordination of women.[48][35] By the 4th and 5th centuries, the Gupta Empire had created in the greater Ganges Plain a complex system of administration and taxation that became a model for later Indian kingdoms.[49][50] Under the Guptas, a renewed Hinduism based on devotion rather than the management of ritual began to assert itself.[51] The renewal was reflected in a flowering of sculpture and architecture, which found patrons among an urban elite.[50]Classical Sanskrit literature flowered as well, and Indian science, astronomy, medicine, and mathematics made significant advances.[50]
Medieval India
The Indian early medieval age, 600 CE to 1200 CE, is defined by regional kingdoms and cultural diversity.[52] When Harsha of Kannauj, who ruled much of the Indo-Gangetic Plain from 606 to 647 CE, attempted to expand southwards, he was defeated by the Chalukya ruler of the Deccan.[53]When his successor attempted to expand eastwards, he was defeated by the Pala king of Bengal.[53] When the Chalukyas attempted to expand southwards, they were defeated by the Pallavas from farther south, who in turn were opposed by the Pandyas and the Cholas from still farther south.[53] No ruler of this period was able to create an empire and consistently control lands much beyond his core region.[52] During this time, pastoral peoples whose land had been cleared to make way for the growing agricultural economy were accommodated within caste society, as were new non-traditional ruling classes.[54] The caste system consequently began to show regional differences.[54]
In the 6th and 7th centuries, the first devotional hymns were created in the Tamil language.[55] They were imitated all over India and led to both the resurgence of Hinduism and the development of all modern languages of the subcontinent.[55] Indian royalty, big and small, and the temples they patronised, drew citizens in great numbers to the capital cities, which became economic hubs as well.[56] Temple towns of various sizes began to appear everywhere as India underwent another urbanisation.[56] By the 8th and 9th centuries, the effects were felt in South-East Asia, as South Indian culture and political systems were exported to lands that became part of modern-day Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam,Philippines, Malaysia, and Java.[57] Indian merchants, scholars, and sometimes armies were involved in this transmission; South-East Asians took the initiative as well, with many sojourning in Indian seminaries and translating Buddhist and Hindu texts into their languages.[57]
After the 10th century, Muslim Central Asian nomadic clans, using swift-horse cavalry and raising vast armies united by ethnicity and religion, repeatedly overran South Asia's north-western plains, leading eventually to the establishment of the Islamic Delhi Sultanate in 1206.[58] The sultanate was to control much of North India, and to make many forays into South India. Although at first disruptive for the Indian elites, the sultanate largely left its vast non-Muslim subject population to its own laws and customs.[59][60] By repeatedly repulsing Mongol raiders in the 13th century, the sultanate saved India from the devastation visited on West and Central Asia, setting the scene for centuries of migration of fleeing soldiers, learned men, mystics, traders, artists, and artisans from that region into the subcontinent, thereby creating a syncretic Indo-Islamic culture in the north.[61][62] The sultanate's raiding and weakening of the regional kingdoms of South India paved the way for the indigenous Vijayanagara Empire.[63] Embracing a strong Shaivite tradition and building upon the military technology of the sultanate, the empire came to control much of peninsular India,[64] and was to influence South Indian society for long afterwards.[63]
Early modern India
In the early 16th century, northern India, being then under mainly Muslim rulers,[65] fell again to the superior mobility and firepower of a new generation of Central Asian warriors.[66] The resulting Mughal Empire did not stamp out the local societies it came to rule, but rather balanced and pacified them through new administrative practices[67][68] and diverse and inclusive ruling elites,[69] leading to more systematic, centralised, and uniform rule.[70] Eschewing tribal bonds and Islamic identity, especially under Akbar, the Mughals united their far-flung realms through loyalty, expressed through a Persianised culture, to an emperor who had near-divine status.[69] The Mughal state's economic policies, deriving most revenues from agriculture[71] and mandating that taxes be paid in the well-regulated silver currency,[72] caused peasants and artisans to enter larger markets.[70] The relative peace maintained by the empire during much of the 17th century was a factor in India's economic expansion,[70] resulting in greater patronage of painting, literary forms, textiles, and architecture.[73] Newly coherent social groups in northern and western India, such as theMarathas, the Rajputs, and the Sikhs, gained military and governing ambitions during Mughal rule, which, through collaboration or adversity, gave them both recognition and military experience.[74] Expanding commerce during Mughal rule gave rise to new Indian commercial and political elites along the coasts of southern and eastern India.[74] As the empire disintegrated, many among these elites were able to seek and control their own affairs.[75] The "single most important power" that emerged in the early modern period was the Maratha confederacy.[76]
By the early 18th century, with the lines between commercial and political dominance being increasingly blurred, a number of European trading companies, including the English East India Company, had established coastal outposts.[77][78] The East India Company's control of the seas, greater resources, and more advanced military training and technology led it to increasingly flex its military muscle and caused it to become attractive to a portion of the Indian elite; both these factors were crucial in allowing the Company to gain control over the Bengal region by 1765 and sideline the other European companies.[79][77][80][81] Its further access to the riches of Bengal and the subsequent increased strength and size of its army enabled it to annex or subdue most of India by the 1820s.[82] India was then no longer exporting manufactured goods as it long had, but was instead supplying the British empire with raw materials, and many historians consider this to be the onset of India's colonial period.[77] By this time, with its economic power severely curtailed by the British parliament and itself effectively made an arm of British administration, the Company began to more consciously enter non-economic arenas such as education, social reform, and culture.[83]
Modern India
Historians consider India's modern age to have begun sometime between 1848 and 1885. The appointment in 1848 of Lord Dalhousie as Governor General of the East India Company set the stage for changes essential to a modern state. These included the consolidation and demarcation of sovereignty, the surveillance of the population, and the education of citizens. Technological changes—among them, railways, canals, and the telegraph—were introduced not long after their introduction in Europe.[84][85][86][87] However, disaffection with the Company also grew during this time, and set off the Indian Rebellion of 1857. Fed by diverse resentments and perceptions, including invasive British-style social reforms, harsh land taxes, and summary treatment of some rich landowners and princes, the rebellion rocked many regions of northern and central India and shook the foundations of Company rule.[88][89] Although the rebellion was suppressed by 1858, it led to the dissolution of the East India Company and to the direct administration of India by the British government. Proclaiming a unitary state and a gradual but limited British-style parliamentary system, the new rulers also protected princes and landed gentry as a feudal safeguard against future unrest.[90][91] In the decades following, public life gradually emerged all over India, leading eventually to the founding of the Indian National Congress in 1885.[92][93][94][95]
The rush of technology and the commercialisation of agriculture in the second half of the 19th century was marked by economic setbacks—many small farmers became dependent on the whims of far-away markets.[96] There was an increase in the number of large-scale famines,[97] and, despite the risks of infrastructure development borne by Indian taxpayers, little industrial employment was generated for Indians.[98] There were also salutary effects: commercial cropping, especially in the newly canalled Punjab, led to increased food production for internal consumption.[99] The railway network provided critical famine relief,[100] notably reduced the cost of moving goods,[100] and helped nascent Indian-owned industry.[99] After World War I, in which some one million Indians served,[101] a new period began. It was marked by British reforms but also repressive legislation, by more strident Indian calls for self-rule, and by the beginnings of a non-violent movement of non-cooperation, of which Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi would become the leader and enduring symbol.[102]During the 1930s, slow legislative reform was enacted by the British; the Indian National Congress won victories in the resulting elections.[103] The next decade was beset with crises: Indian participation in World War II, the Congress's final push for non-cooperation, and an upsurge of Muslim nationalism. All were capped by the advent of independence in 1947, but tempered by the partition of India into two states: India and Pakistan.[104]
Vital to India's self-image as an independent nation was its constitution, completed in 1950, which put in place a secular and democratic republic.[105] In the 60 years since, India has had a mixed record of successes and failures.[106] It has remained a democracy with civil liberties, an active Supreme Court, and a largely independent press.[106] Economic liberalisation, which was begun in the 1990s, has created a large urban middle class, transformed India into one of the world's fastest-growing economies,[107] and increased its geopolitical clout. Indian movies, music, and spiritual teachings play an increasing role in global culture.[106] Yet, India is also shaped by seemingly unyielding poverty, both rural and urban;[106] by religious and caste-related violence;[108] by Maoist-inspired Naxalite insurgencies;[109] and by separatism in Jammu and Kashmir and in Northeast India.[110] It has unresolved territorial disputes with China,[111] and with Pakistan.[111] The India–Pakistan nuclear rivalry came to a head in 1998.[112] India's sustained democratic freedoms are unique among the world's new nations; however, in spite of its recent economic successes, freedom from want for its disadvantaged population remains a goal yet to be achieved.[113]
Geography
Main article: Geography of India
See also: Geology of India
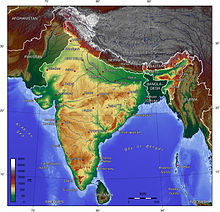
India comprises the bulk of the Indian subcontinent, lying atop the Indian tectonic plate, and part of the Indo-Australian Plate.[114] India's defining geological processes began 75 million years ago when the Indian plate, then part of the southern supercontinent Gondwana, began a north-eastward drift caused by seafloor spreading to its south-west, and later, south and south-east.[114] Simultaneously, the vast Tethynoceanic crust, to its northeast, began to subduct under the Eurasian plate.[114] These dual processes, driven by convection in the Earth'smantle, both created the Indian Ocean and caused the Indian continental crust eventually to under-thrust Eurasia and to uplift theHimalayas.[114] Immediately south of the emerging Himalayas, plate movement created a vast trough that rapidly filled with river-borne sediment[115] and now constitutes the Indo-Gangetic Plain.[116] Cut off from the plain by the ancient Aravalli Range lies the Thar Desert.[117]
The original Indian plate survives as peninsular India, the oldest and geologically most stable part of India. It extends as far north as theSatpura and Vindhya ranges in central India. These parallel chains run from the Arabian Sea coast in Gujarat in the west to the coal-richChota Nagpur Plateau in Jharkhand in the east.[118] To the south, the remaining peninsular landmass, the Deccan Plateau, is flanked on the west and east by coastal ranges known as the Western and Eastern Ghats;[119] the plateau contains the country's oldest rock formations, some over one billion years old. Constituted in such fashion, India lies to the north of the equator between 6° 44' and 35° 30' north latitude[e]and 68° 7' and 97° 25' east longitude.[120]
India's coastline measures 7,517 kilometres (4,700 mi) in length; of this distance, 5,423 kilometres (3,400 mi) belong to peninsular India and 2,094 kilometres (1,300 mi) to the Andaman, Nicobar, and Lakshadweep island chains.[121] According to the Indian naval hydrographic charts, the mainland coastline consists of the following: 43% sandy beaches; 11% rocky shores, including cliffs; and 46% mudflats or marshy shores.[121]
Major Himalayan-origin rivers that substantially flow through India include the Ganges and the Brahmaputra, both of which drain into the Bay of Bengal.[122] Important tributaries of the Ganges include the Yamuna and the Kosi; the latter's extremely low gradient often leads to severe floods and course changes.[123] Major peninsular rivers, whose steeper gradients prevent their waters from flooding, include the Godavari, the Mahanadi, the Kaveri, and the Krishna, which also drain into the Bay of Bengal;[124] and the Narmada and the Tapti, which drain into theArabian Sea.[125] Coastal features include the marshy Rann of Kutch of western India and the alluvial Sundarbans delta of eastern India; the latter is shared with Bangladesh.[126] India has two archipelagos: the Lakshadweep, coral atolls off India's south-western coast; and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a volcanic chain in the Andaman Sea.[127]
The Indian climate is strongly influenced by the Himalayas and the Thar Desert, both of which drive the economically and culturally pivotal summer and winter monsoons.[128] The Himalayas prevent cold Central Asian katabatic winds from blowing in, keeping the bulk of the Indian subcontinent warmer than most locations at similar latitudes.[129][130] The Thar Desert plays a crucial role in attracting the moisture-laden south-west summer monsoon winds that, between June and October, provide the majority of India's rainfall.[128] Four major climatic groupings predominate in India: tropical wet, tropical dry, subtropical humid, and montane.[131]
Biodiversity
Main article: Wildlife of India
India lies within the Indomalaya ecozone and contains three biodiversity hotspots.[133] One of 17 megadiverse countries, it hosts 8.6% of all mammalian, 13.7% of all avian, 7.9% of all reptilian, 6% of all amphibian, 12.2% of all piscine, and 6.0% of all flowering plant species.[134][135] Endemism is high among plants, 33%, and among ecoregions such as the shola forests.[136] Habitat ranges from thetropical rainforest of the Andaman Islands, Western Ghats, and North-East India to the coniferous forest of the Himalaya. Between these extremes lie the moist deciduous sal forest of eastern India; the dry deciduous teak forest of central and southern India; and the babul-dominated thorn forest of the central Deccan and western Gangetic plain.[137] Under 12% of India's landmass bears thick jungle.[138] The medicinal neem, widely used in rural Indian herbal remedies, is a key Indian tree. The luxuriant pipal fig tree, shown on the seals of Mohenjo-daro, shaded Gautama Buddha as he sought enlightenment.
Many Indian species descend from taxa originating in Gondwana, from which the Indian plate separated more than 105 million years before present.[139] Peninsular India's subsequent movement towards and collision with the Laurasian landmass set off a mass exchange of species. Epochal volcanism and climatic changes 20 million years ago forced a mass extinction.[140] Mammals then entered India from Asia through two zoogeographical passes flanking the rising Himalaya.[137] Thus, while 45.8% of reptiles and 55.8% of amphibians are endemic, only 12.6% of mammals and 4.5% of birds are.[135] Among them are the Nilgiri leaf monkey and Beddome's toad of the Western Ghats. India contains 172 IUCN-designated threatened animal species, or 2.9% of endangered forms.[141] These include the Asiatic lion, the Bengal tiger, and the Indian White-rumped vulture, which, by ingesting the carrion of diclofenac-laced cattle, nearly went extinct.
The pervasive and ecologically devastating human encroachment of recent decades has critically endangered Indian wildlife. In response the system of national parks and protected areas, first established in 1935, was substantially expanded. In 1972, India enacted the Wildlife Protection Act[142] and Project Tiger to safeguard crucial wilderness; the Forest Conservation Act was enacted in 1980 and amendments added in 1988.[143] India hosts more than five hundred wildlife sanctuaries and thirteen biosphere reserves,[144] four of which are part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves; twenty-five wetlands are registered under the Ramsar Convention.[145]
Politics
Main article: Politics of India
India is the world's most populous democracy.[146] A parliamentary republic with a multi-party system,[147] it has six recognised national parties, including the Indian National Congress and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), and more than 40 regional parties.[148] The Congress is considered centre-left or "liberal" in Indian political culture, and the BJP centre-right or "conservative". For most of the period between 1950—when India first became a republic—and the late 1980s, the Congress held a majority in the parliament. Since then, however, it has increasingly shared the political stage with the BJP,[149] as well as with powerful regional parties which have often forced the creation of multi-party coalitions at the centre.[150]
In the Republic of India's first three general elections, in 1951, 1957, and 1962, the Jawaharlal Nehru-led Congress won easy victories. On Nehru's death in 1964, Lal Bahadur Shastri briefly became prime minister; he was succeeded, after his own unexpected death in 1966, byIndira Gandhi, who went on to lead the Congress to election victories in 1967 and 1971. Following public discontent with the state of emergency she declared in 1975, the Congress was voted out of power in 1977; the then-new Janata Party, which had opposed the emergency, was voted in. Its government lasted just over three years. Voted back into power in 1980, the Congress saw a change in leadership in 1984, when Indira Gandhi was assassinated; she was succeeded by her son Rajiv Gandhi, who won an easy victory in the general elections later that year. The Congress was voted out again in 1989 when a National Front coalition, led by the newly formed Janata Dal in alliance with the Left Front, won the elections; that government too proved relatively short-lived: it lasted just under two years.[151]Elections were held again in 1991; no party won an absolute majority. But the Congress, as the largest single party, was able to form aminority government led by P. V. Narasimha Rao.[152]
A two-year period of political turmoil followed the general election of 1996. Several short-lived alliances shared power at the centre. The BJP formed a government briefly in 1996; it was followed by two comparatively long-lasting United Front coalitions, which depended on external support. In 1998, the BJP was able to form a successful coalition, the National Democratic Alliance (NDA). Led by Atal Bihari Vajpayee, the NDA became the first non-Congress, coalition government to complete a five-year term.[153] In the 2004 Indian general elections, again no party won an absolute majority, but the Congress emerged as the largest single party, forming another successful coalition: the United Progressive Alliance (UPA). It had the support of left-leaning parties and MPs who opposed the BJP. The UPA returned to power in the 2009 general election with increased numbers, and it no longer required external support from India's communist parties.[154] That year, Manmohan Singh became the first prime minister since Jawaharlal Nehru in 1957and 1962 to be re-elected to a consecutive five-year term.[155] In the 2014 general election, Bharatiya Janata Party became the first political party since 1984 to win a majority and govern without the support of other parties.[156]
Government
Main article: Government of India
See also: Elections in India
India is a federation with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. It is a constitutional republic andrepresentative democracy, in which "majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law". Federalism in India defines the power distribution between the federal government and the states. The government abides by constitutional checks and balances. The Constitution of India, which came into effect on 26 January 1950,[157] states in its preamble that India is a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic.[158] India's form of government, traditionally described as "quasi-federal" with a strong centre and weak states,[159] has grown increasingly federal since the late 1990s as a result of political, economic, and social changes.[160][161]
| Flag | Tricolour |
| Emblem | Sarnath Lion Capital |
| Anthem | Jana Gana Mana |
| Song | Vande Mataram |
| Currency | |
| Calendar | Saka |
| Game | Not declared[162] |
| Flower | Lotus |
| Fruit | Mango |
| Tree | Banyan |
| Bird | Indian Peafowl |
| Land animal | Tiger |
| Aquatic animal | River Dolphin |
| River | Ganga or Ganges |
The federal government comprises three branches:
- Executive: The President of India is the head of state[163] and is elected indirectly by a national electoral college[164] for a five-year term.[165] The Prime Minister of India is the head of government and exercises most executive power.[166] Appointed by the president,[167] the prime minister is by convention supported by the party or political alliance holding the majority of seats in the lower house of parliament.[166] The executive branch of the Indian government consists of the president, the vice-president, and the Council of Ministers—the cabinet being its executive committee—headed by the prime minister. Any minister holding a portfolio must be a member of one of the houses of parliament.[163] In the Indian parliamentary system, the executive is subordinate to the legislature; the prime minister and his council are directly responsible to the lower house of the parliament.[168]
- Legislative: The legislature of India is the bicameral parliament. It operates under a Westminster-style parliamentary system and comprises the upper house called the Rajya Sabha ("Council of States") and the lower called the Lok Sabha ("House of the People").[169] The Rajya Sabha is a permanent body that has 245 members who serve in staggered six-year terms.[170] Most are elected indirectly by the state and territorial legislatures in numbers proportional to their state's share of the national population.[167] All but two of the Lok Sabha's 545 members are directly elected by popular vote; they represent individual constituencies via five-year terms.[171] The remaining two members are nominated by the president from among the Anglo-Indian community, in case the president decides that they are not adequately represented.[172]
- Judicial: India has a unitary three-tier independent judiciary[173] that comprises the Supreme Court, headed by the Chief Justice of India, 24 High Courts, and a large number of trial courts.[173] The Supreme Court has original jurisdiction over cases involvingfundamental rights and over disputes between states and the centre; it has appellate jurisdiction over the High Courts.[174] It has the power both to declare the law and to strike down union or state laws which contravene the constitution.[175] The Supreme Court is also the ultimate interpreter of the constitution.[176]
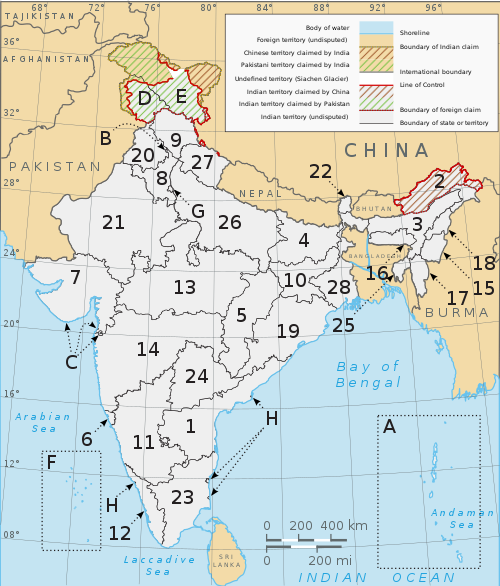
Subdivisions
India is a federation composed of 29 states and 7 union territories.[177] All states, as well as the union territories of Puducherry and the National Capital Territory of Delhi, have elected legislatures and governments, both patterned on the Westminster model. The remaining five union territories are directly ruled by the centre through appointed administrators. In 1956, under the States Reorganisation Act, states were reorganised on a linguistic basis.[178] Since then, their structure has remained largely unchanged. Each state or union territory is further divided into administrative districts. The districts in turn are further divided into tehsils and ultimately into villages.
States








No comments:
Post a Comment